Nephron stock illustration. Illustration of anatomy, diuretics 47649327
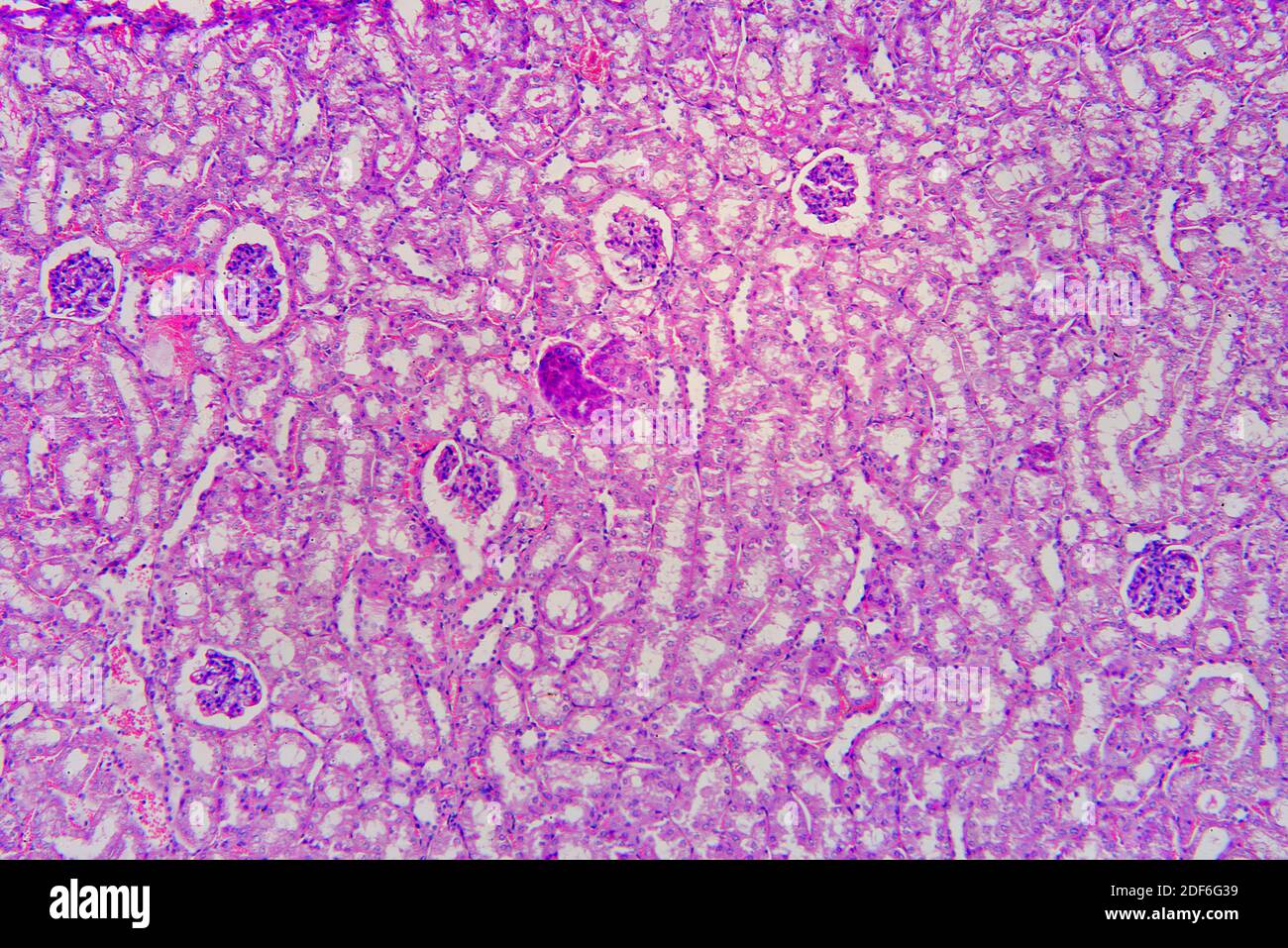
Kidney section showing nephrons, Bowman capsules, glomerulus and distal
The renal structures that conduct the essential work of the kidney cannot be seen by the naked eye. Only a light or electron microscope can reveal these structures. Even then, serial sections and computer reconstruction are necessary to give us a comprehensive view of the functional anatomy of the nephron and its associated blood vessels.
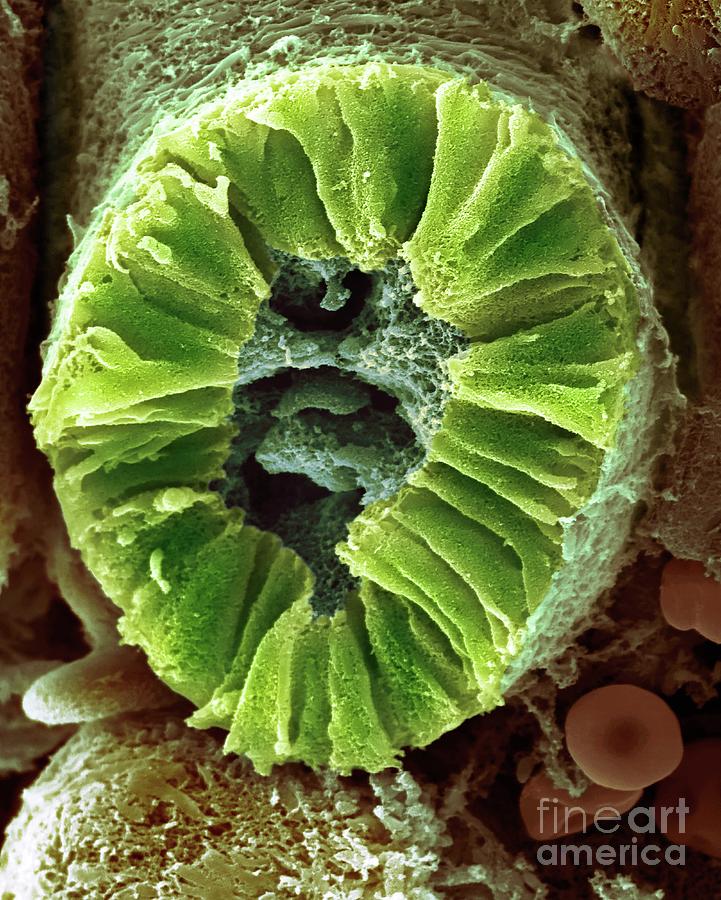
Human Kidney Nephron Photograph by Dennis Kunkel Microscopy/science
Scanning electron microscopy was used to study the ultrastructural morphology of the nephron. Material for observation was taken from rat kidneys which were fixed by vascular perfusion. Different techniques for splitting open the kidney, combined with stereoscopic viewing, provided many instructive views of nephron morphology.
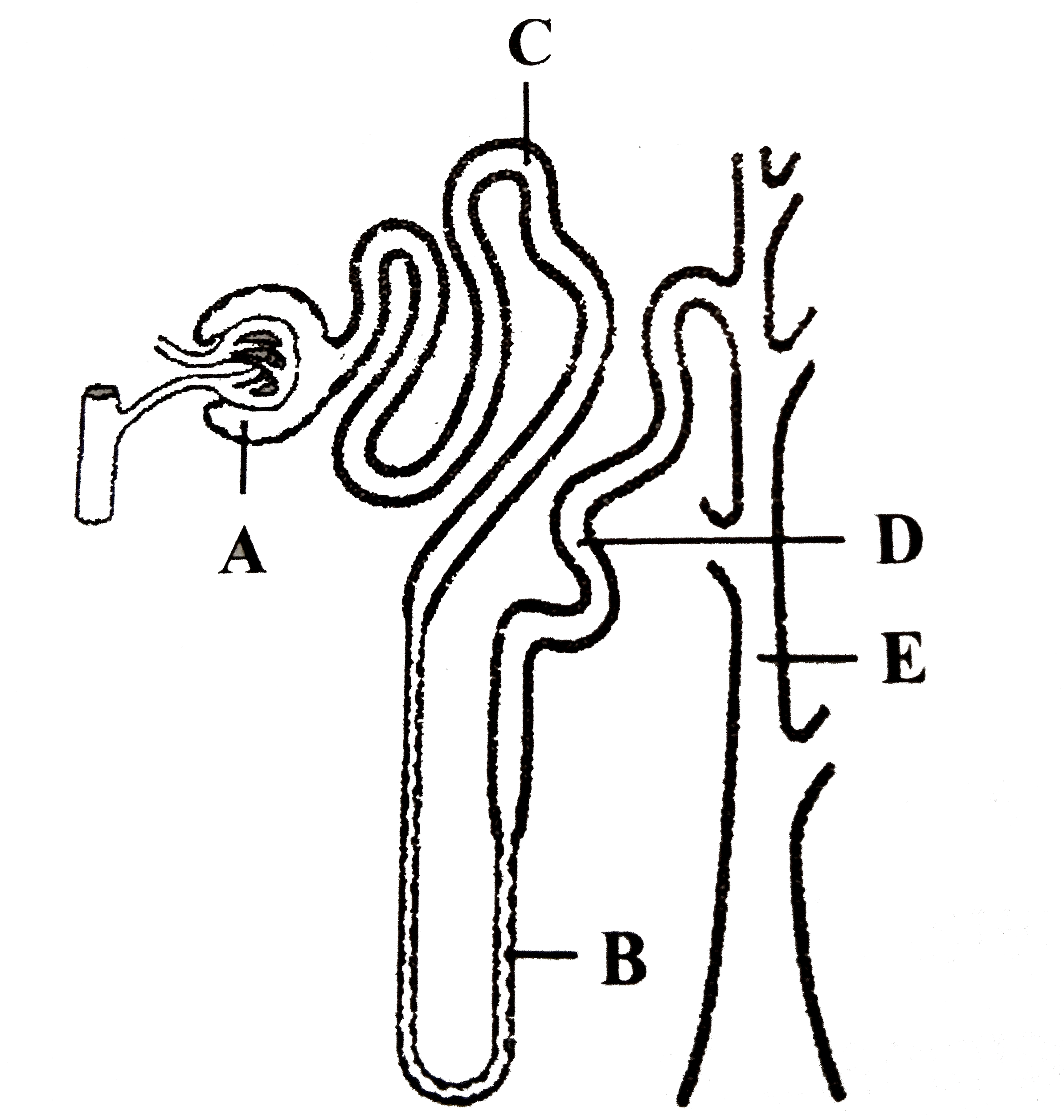
Structure Of Nephron Class 11 Jami of All Trades
Microanatomy of the Nephron Renal Corpuscle. As discussed earlier, the renal corpuscle consists the glomerulus and the glomerular capsule. The glomerulus is a high pressured, fenestrated capillary with large holes (fenestrations) between the endothelial cells.The glomerular capsule captures the filtrate created by the glomerulus and directs this filtrate to the PCT.
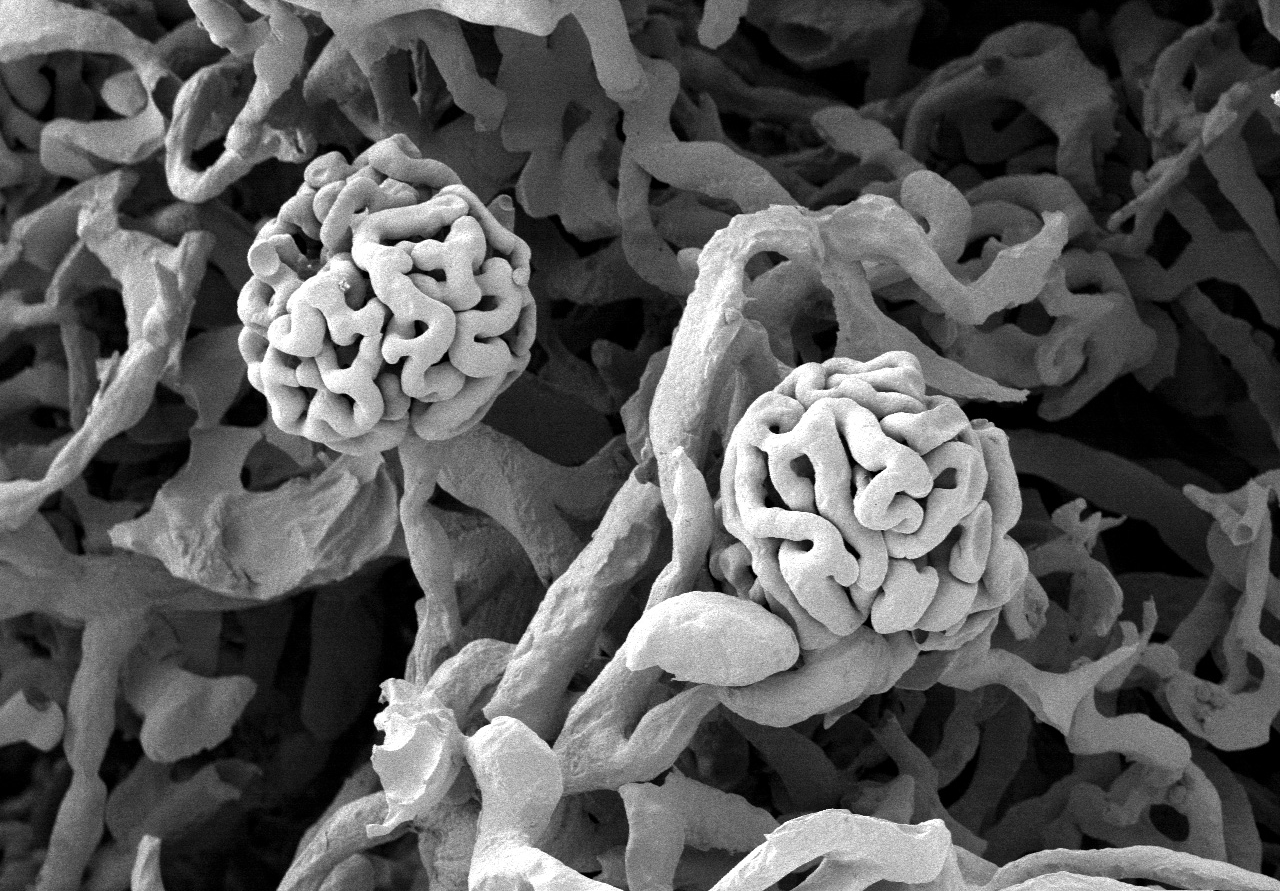
Scanning Electron Microscopy of Corrosion Casts
Symposium on Renal Physiology Electron Microscopy of the Kidney' JOHANNES RHODIN, M.D. New York, New York THE structure of the nephron includes a great variety of cell types, from the complicated composition of the filtering glomerular capillary membrane to the relatively simple and pale cells of the collecting ducts.

Pin on Anatomy Images
Download the Temu App and start saving more today! Unleash incredible deals and coupons. Ready to shop and save? Explore amazing deals on the Temu App. Free shipping & return.

Nephron stock illustration. Illustration of anatomy, diuretics 47649327
To this purpose, we took advantage of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), an imaging approach rarely used for patients 15, which provides a global visualization of the actual three-dimensional.

Nephrons in your kidneys Interior del cuerpo humano, Anatomia
The nephron is composed of the glomerulus, the juxtaglomerular complex, the proximal convoluted tubule, the loop of Henle and the distal convoluted tubule. This chapter deals with the light and electron microscopic structure of both the connective tissue capsule and the uriniferous tubule in the parenchyma of the mammalian kidney. Keywords
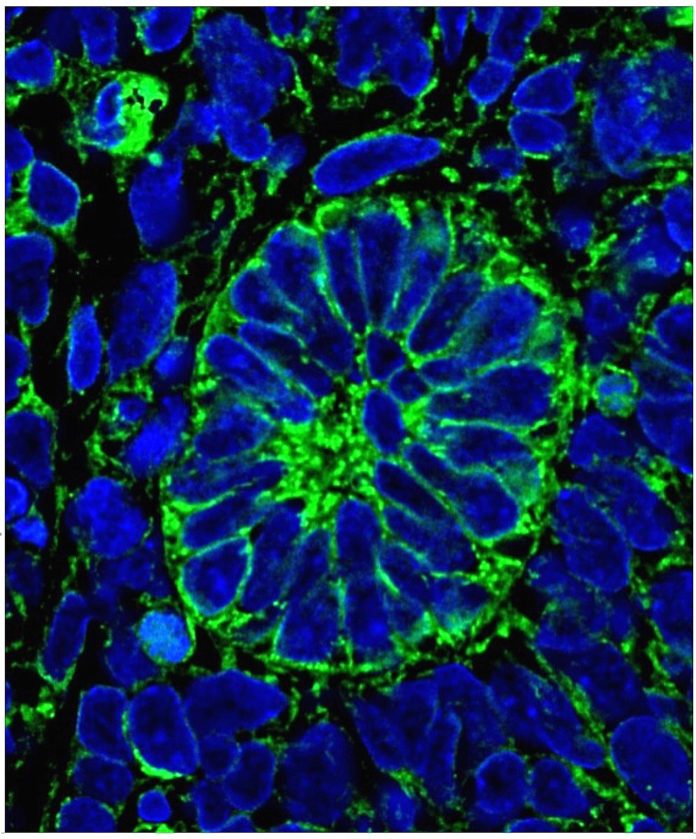
Scientists devised functioning kidney tissue
Scanning electron microscopy revealed a number of new features including the complex organization and structure of kidney podocytes; the distribution of endothelial pores and the presence of endothelium microprojections and branching endothelial thickenings. Scanning electron microscopy was used to study the ultrastructural morphology of the nephron. Material for observation was taken from rat.

Electron microscope radioautographs of portions of the rat nephron
Understand the structure and function of the nephron and know the roles of the glomerulus, proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule, and collecting duct on urine formation and composition.. PAS stain, ×400) and wide foot process effacement (electron microscope, upper middle panel, ×2500). The second biopsy performed at age.

The nephron has five regions.
1/4. Synonyms: Cortex renalis. The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs of the urinary system. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. The nephron is the main functional unit of the kidney, in charge of removing metabolic waste and excess water from the blood.

Selfassembly of renal nephronlike tubules. (a) Fluorescence
The final part of the nephron is the connecting tubules, where the last fine-tuning of the urine occurs. These tubules have two types of cells; the intercalated cells and the connecting tubule (CNT) cells. The intercalated cells appear dense on electron microscopy and do not have the basolateral amplification characteristic of the DCT cells.

Transmission electron microscopy showing the presence of specific
The renal structures that conduct the essential work of the kidney cannot be seen by the naked eye. Only a light or electron microscope can reveal these structures. Even then, serial sections and computer reconstruction are necessary to give us a comprehensive view of the functional anatomy of the nephron and its associated blood vessels.
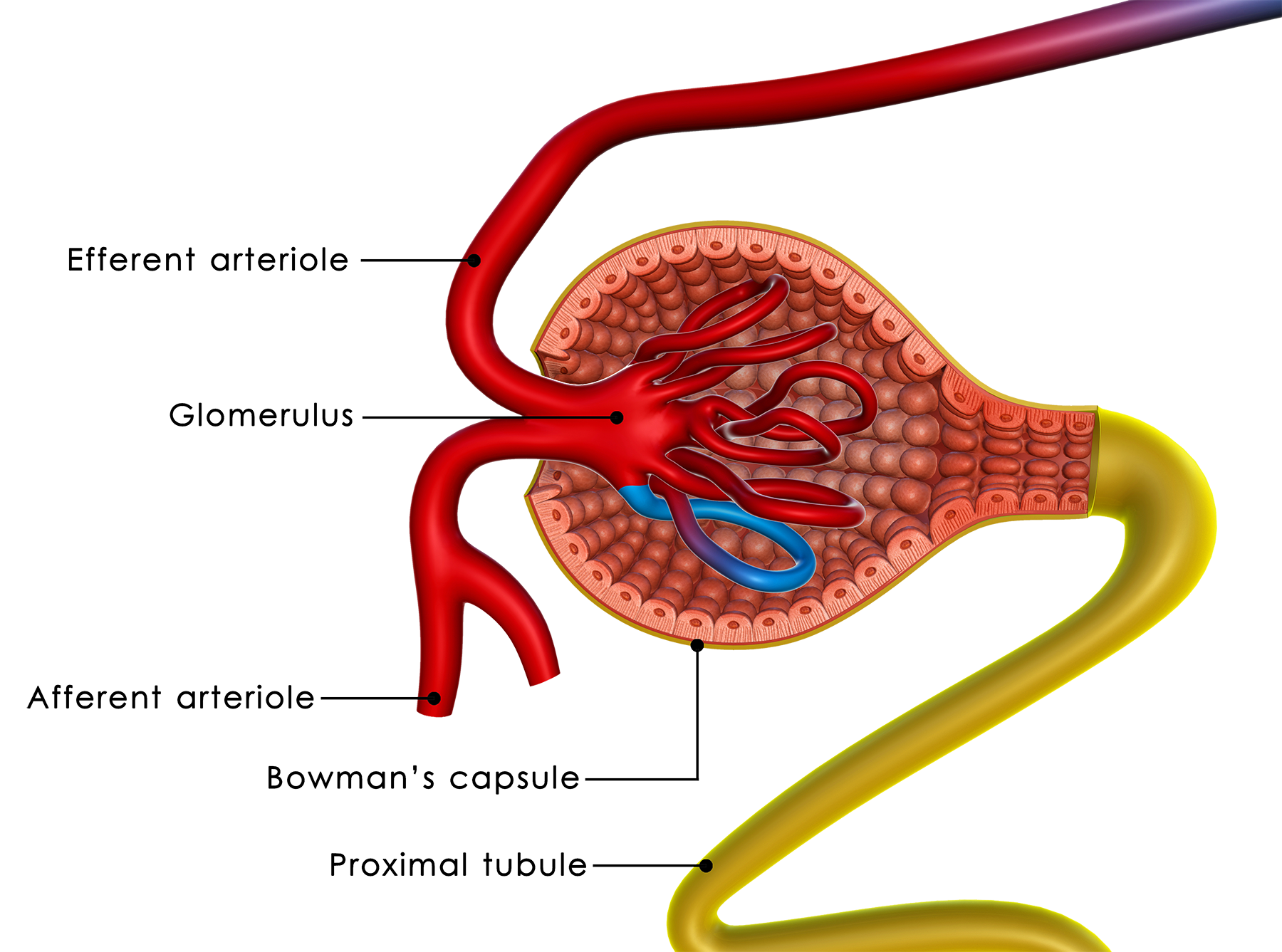
The Structure and Function of the Nephron Made Easy InteractiveBiology
The first attempt to overcome the resolution limit of light and fluorescence microscopes was in 1931 when Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll invented the electron microscope (EM), which uses a beam of accelerated electrons, instead of a beam of light, as an excitation source, and has a higher resolving power than light microscopes (up to 0.2 nm).

17 Best images about Kidney on Pinterest Medicine, Loop of henle and
75 of The Top 100 Retailers Can Be Found on eBay. Find Great Deals from the Top Retailers. Looking For Electron? We Have Almost Everything on eBay.

The Urinary System Kidneys
Panel c shows scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-ray analyzer (SEM-EDX) mapping of the wafers. In the wafer shown (Na selective wafer), it is seen that the wafer before the run has a.

Electron micrographs of the proximal and distal tubules of a nephron
Scanning electron microscopy was used to study the ultrastructural morphology of the nephron. Material for observation was taken from rat kidneys which were fixed by vascular perfusion. Different techniques for splitting open the kidney, combined with stereoscopic viewing, provided many instructive views of nephron morphology. In addition.