Water footprint of Xining 2018 (a) overall structure of water... Download Scientific Diagram
Beyond the Water Cycle Teaching About Water Footprints
The blue water footprint is defined as the consumption of water originating in blue water resources such as surface- and groundwater. From: Assessing and Measuring Environmental Impact and Sustainability, 2015 View all Topics Add to Mendeley About this page Overview of environmental footprints Lidija Čuček,.

Understanding the impact of our water footprint
Water Footprint Assessment is a four-phase process that quantifies and maps green, blue and grey water footprints, assesses the sustainability, efficiency and equitability of water use and identifies which strategic actions should be prioritised in order to make a footprint sustainable.

Was ist ein Wasserfußabdruck? WorldAtlas
The (consumptive) water footprint of HDPE balls. HDPE is a solid fossil fuel transformed using crude oil, natural gas and electricity 8, 9. Given the blue water footprint of these natural.

How to Help the Environment by Reducing Your Water Footprint
Water plays a central role in supporting agriculture, with food production responsible for ~90% of humanity's consumptive water footprint 1, 2. Accurately assessing demands for freshwater.

Corporate Water Footprints Explained Infographic FigBytes
where Resource Use and Emissions represent food-related energy use, blue water footprint, and GHG emissions associated with actual (A) and recommended (R) Calories consumed within each food group, i, by American adults, age 19 plus.For our study, actual Caloric consumption (or actual Calories consumed) refers to the sum of actual Calories eaten (or the actual Caloric intake) plus the.

What is Water footprint?
To quantify the role of water loss from multipurpose reservoirs, the term blue water footprint (BWF; Egan 2011, Hoekstra and Mekonnen 2012) is adopted in this study. Blue water refers to the surface water and/or groundwater which is utilized to generate a product.

Water Footprint How Much Water it Takes to Make Things Sustainable Warriors
Blue water footprint and blue water availability are expressed in mm/month. For each month of the year we consider the ten-year average for the period 1996-2005 to incorporate climate variability, while acknowledging that averaging can obscure inter-annual variability in scarcity. Average monthly blue water footprints per river basin for the

What Is a Water Footprint? Sphera
Here we quantify and map at a 5-arcmin spatial resolution the blue water footprint of each country's national consumption and where they infringe sustainable environmental flows as defined by the.

Research duo maps worldwide water footprint with high spatial resolution
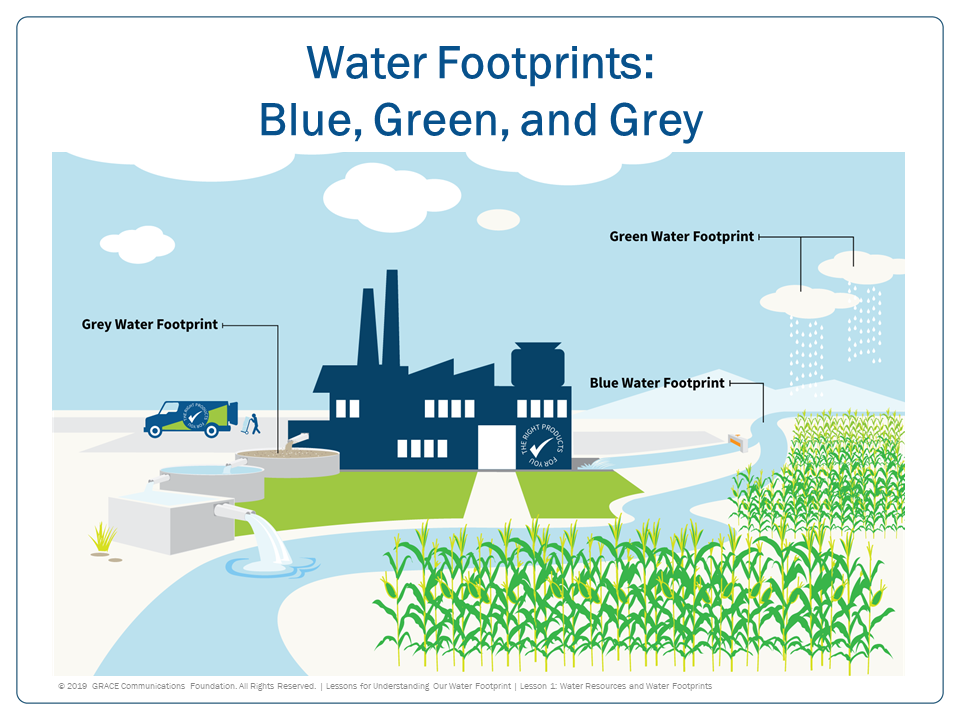
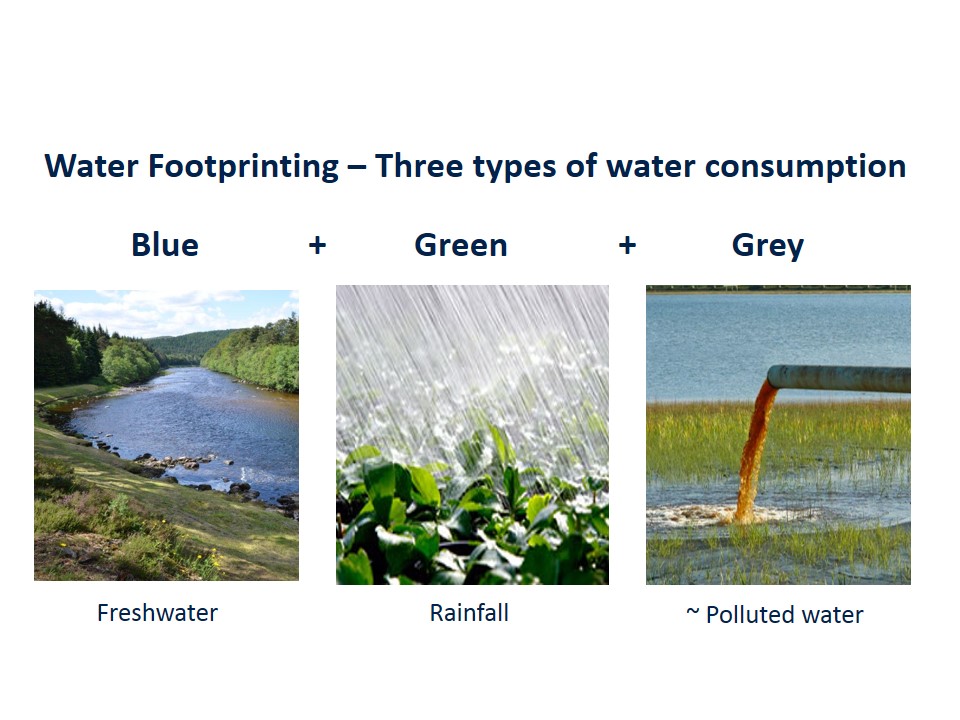
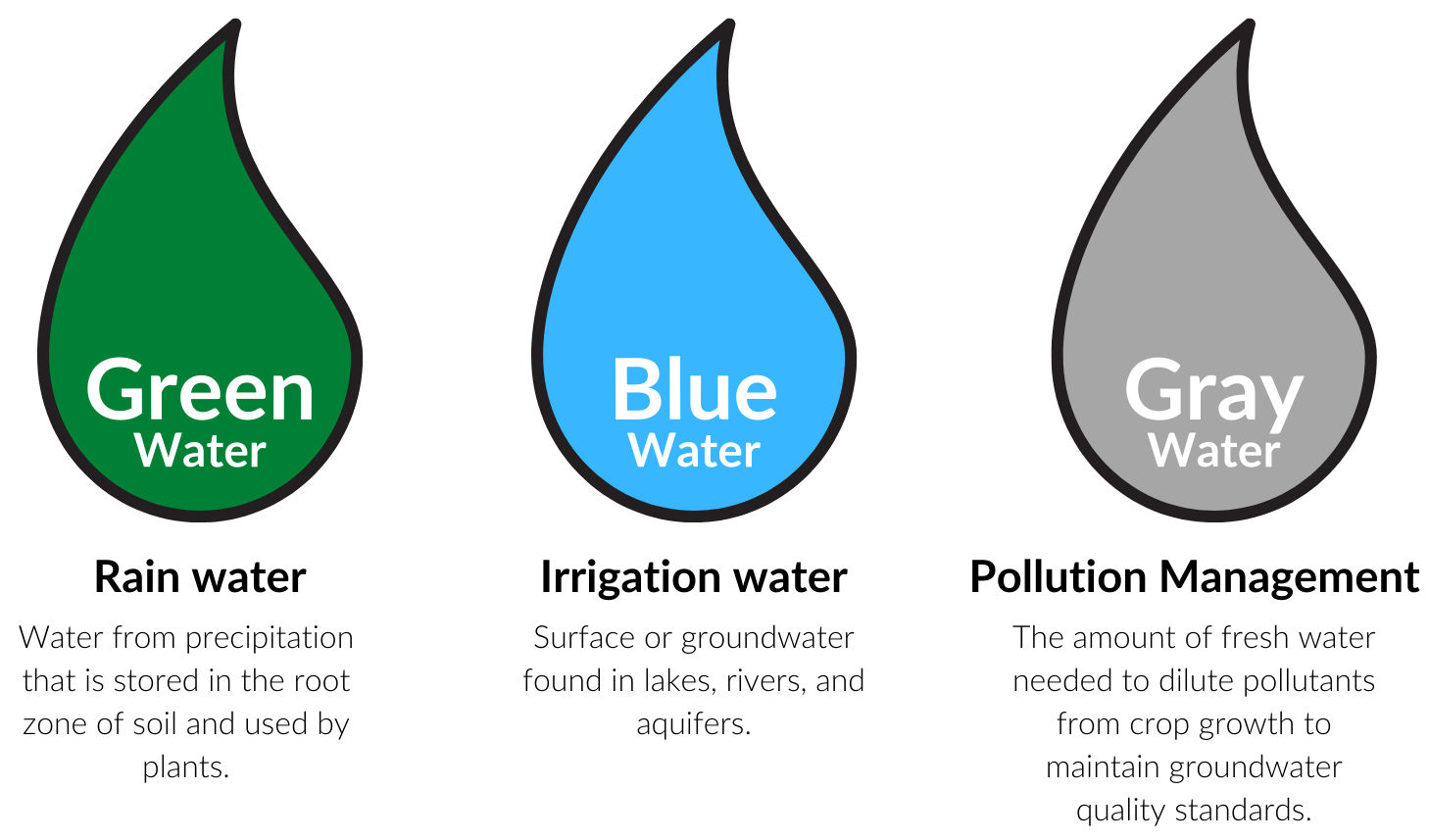
Blue Water Footprint: The amount of surface water and groundwater required (evaporated or used directly) to produce an item. Green Water Footprint: The amount of rainwater required (evaporated or used directly) to make an item.

The water footprint Environmental Footprint
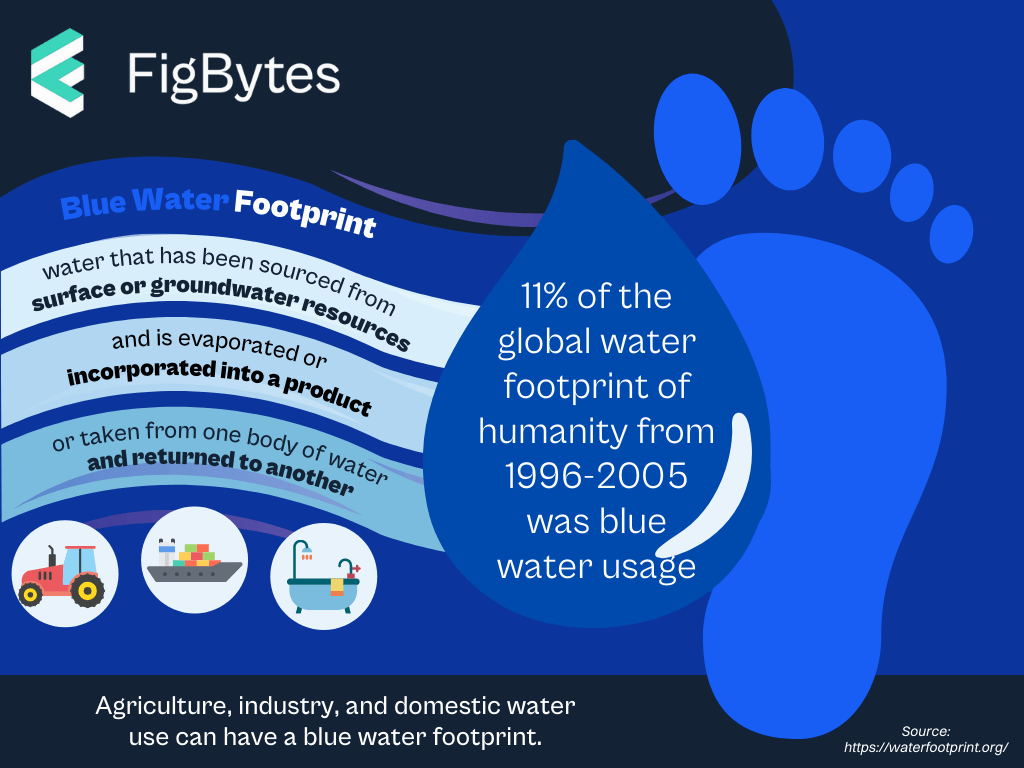
Blue water footprint refers to the amount of fresh surface or groundwater used to produce a product or service. This can include water used in irrigation, manufacturing, or other processes. It is an important consideration in sustainable resource management and understanding the environmental impact of human activities.

Water Footprint Royalty Free Stock Image Image 7263386
Blue water footprint is water that has been sourced from surface or groundwater resources and is either evaporated, incorporated into a product or taken from one body of water and returned to another, or returned at a different time. Irrigated agriculture, industry and domestic water use can each have a blue water footprint.
Water Footprint Network Using the Water Footprint Concept to Promote Sustainable, Fair, and
Blue water footprint Blue water footprint impact index Blue water scarcity Business water footprint Corporate water footprint Critical load Crop water requirement Crop yield Dilution factor Direct water footprint Effective precipitation End-use water footprint of a product Environmental flow requirements Environmental green water requirement
New Water Footprint Standard Published ISO 14046 Circular Ecology
In this equation, blue water scarcity (WS blue) is defined as the size of the human blue water footprint in a catchment x at time t divided by the blue water produced by nature (R nat) less the environmental flow requirement (EFR) in catchment x at time t. What this means is that a blue water scarcity value of 1 or 100% represents blue water.

Promoting water sustainability of financial… Green Economy Coalition
Blue water footprint refers to the volume of fresh surface and groundwater that has been evaporated or incorporated into a product. Blue water footprint is unsustainable when it exceeds the available renewable blue water, thereby violating the environmental flow standard and depleting groundwater. Jägermeyr et al. (Jägermeyr et al., 2017.
What Is a Water Footprint? Water Footprints Explained FigBytes
Increasing pressure on the world's freshwater resources raises serious concerns about global food security and the sustainability of water use in agriculture. Here we quantify and map at a 5-arcmin spatial resolution the blue water footprint of each country's national consumption and where they infringe sustainable environmental flows as defined by the presumptive environmental flow.

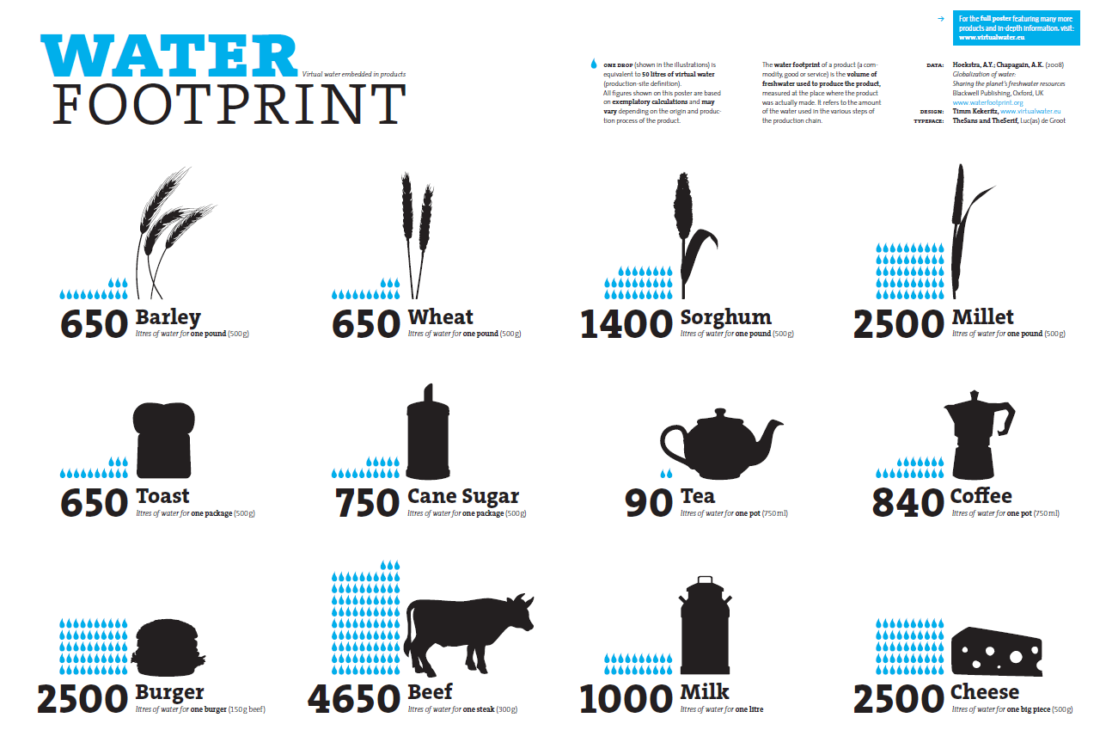
The Water Footprint of Food
The blue water footprint (BWF) refers to the volume of consumptive freshwater use for irrigation that comes from surface water and groundwater. Blue water availability is taken from FAO (2015) and refers to the total renewable amount (internal and external resources), which is the long-term average annual flow of rivers (surface water) and.